Table of Contents
How Long Does Adderall Stay in Your System? Everything You Need to Know
How long does 10mg Adderall stay in your system?What does Adderall test positive for?Will Adderall cause me to fail a drug test?Is Adderall addicting?how long does 20mg of adderall last,does adderall build up in your system,does adderall show up on a drug test for a job,how long does 5mg adderall stay in your system,adderall side effects,how long does adderall take to kick in on an empty stomach,r3060 how long does it last,does exercise make adderall wear off,how long does 20mg of adderall last,does adderall build up in your system,how long does adderall withdrawal last,does adderall show up on a drug test for a job reddit,how long does 10mg adderall stay in your system,how long does 5mg adderall stay in your system
Adderall is a brand name for a category of drug that is frequently employed in the management of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (ADHD). It’s an amphetamine, a sort of stimulant that acts on the central nervous system and makes you feel more energized.
Stimulants available by prescription, such as Adderall, are said to alleviate the symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in 70 to 80 percent of children and in 70 percent of adults.
Adderall is also utilized for the treatment of certain sleep disorders, including narcolepsy. Off-label uses include treating severe depression using it.
Adderall has a significant risk of being abused by users. People who do not have a prescription from a physician can use it to improve their ability to concentrate and pay attention.
Continue reading to learn how this medication functions, how long its effects normally last in your body, and any possible adverse reactions they may cause.
How quickly does it get rid of itself in your body?
The digestive system is responsible for the absorption of Adderall. Following this, it is metabolized, or broken down, in your liver, and then excreted out of your body in your urine.
Adderall is eliminated through the urine, but because it operates throughout the body, it can be detected in a number of other ways, as will be shown in the following paragraphs.
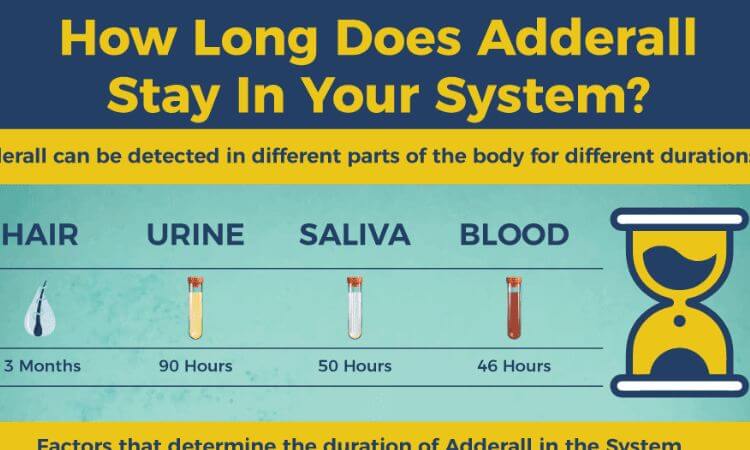
A blood test can identify Adderall in the bloodstream up to 46 hours after the last time it was used. After using Adderall, there is a greater likelihood that it will show up in blood testing.
It is possible to detect Adderall in your urine for approximately 48 to 72 hours after your last usage of the drug. Due to the fact that Adderall is removed through urine, the results of this test will typically reveal a higher concentration of the substance than those of other drug tests.
20 to 50 hours after the last time someone used Adderall, the drug can still be found in their saliva.
Drug testing using hair is not a very popular approach, although it can detect Adderall use for up to three months after it has been discontinued.
Up to 46 hours after use, blood can still be detected.
Urine: Can be tested for up to three days following use.
Detectable in saliva anywhere between 20 and 50 hours after use.
Hair: Possibility of detection up to three months after treatment has ended.
What are some of the factors that can influence how long it stays in your body?
The rate at which Adderall is metabolized, or broken down and eliminated from the body, varies greatly between individuals. Adderall’s half-life, or the amount of time it spends in your body before being broken down into its component parts by your metabolism, is subject to a wide range of variable influences.
DO NOT MISS: How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System? Everything You Need to Know
Composition of the body
The amount of time that Adderall remains in your system is also influenced by your body composition, which includes your total weight, the amount of body fat you have, and your height. This is due in part to the fact that larger persons typically require higher drug doses, which means the medication takes a long time to exit their bodies.
Nevertheless, there is some evidence to support this.
Drugs like Adderall, which are metabolized by a certain liver pathway, clear from the body faster in people who weigh more or have more body fat, according to a trusted source. This is the case even after taking into consideration the amount that is appropriate for the individual’s body weight.
Metabolism
To put it another way, everyone’s liver contains enzymes that can metabolize, or break down, substances like Adderall. Your metabolic rate can be influenced by a wide variety of factors, including your amount of physical activity, your gender, and the various medications you take.
The length of time a drug remains in your body is influenced by your metabolism; the quicker it is metabolized, the quicker it will be eliminated from your body.
Dosage
Adderall is offered in a wide range of dosage strengths, with tablet or capsule forms ranging from 5 mg to 30 mg in strength. The longer it may take for your body to completely metabolize Adderall, the larger the dose of the medication you take. Because of this, bigger doses will remain in your body for a longer period of time.
There is an instant release version of Adderall as well as an extended-release version, and these two formulations dissolve in the body at significantly different rates. Because of this, the amount of time the medicine remains in your system may be altered.
Age
It may take longer for drugs to be eliminated from your system if you are an older adult. This is for a number of different causes.
Because the size of your liver shrinks with age, it may take your liver a longer period of time to completely break down Adderall if you are an older person.
Urine production naturally drops off as people become older. Conditions that are associated with aging, such as cardiovascular disease, can also cause a decline in kidney function. Both of these things can contribute to a medication’s persistence in the body for a longer period of time.
As you become older, your body composition shifts, which can result in variations in the rate at which your body metabolizes drugs and eliminates them from its system.
The gastrointestinal tract is the site of Adderall absorption; the liver is responsible for its subsequent metabolism, and the kidneys are responsible for its elimination. It is possible that it will take longer for Adderall to be eliminated from your body if any of these organs or systems are not working properly.
How does Adderall work?
Adderall is effective because it stimulates the central nervous system, which would seem to go against common sense.
People who suffer from ADHD are thought to have insufficient levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine in their frontal lobes, also known as the “reward center” of the brain. Because of this, people could have a tendency to look for ways to stimulate their frontal lobes and experience the pleasant feeling that comes along with having dopamine in their system. This may lead to them engaging in conduct that is impulsive or thrill-seeking, or it may cause them to get easily sidetracked.
Adderall works to enhance the amount of dopamine that is accessible in the frontal lobe by acting as a stimulant on the central nervous system. People who have ADHD are able to put more effort into their work as a result of this treatment since it prevents them from seeking stimulus.
Medication is typically only one component of a comprehensive treatment strategy for ADHD, which also typically includes behavioral therapy, educational and organizational support, as well as other lifestyle strategies.
YOU MAY LIKE THIS: How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Your System? Everything You Need to Know
Concomitant effects
An overdose of Adderall can result in a variety of unpleasant and potentially harmful adverse effects, including the following:
| headache | hyperventilation |
| dry mouth | pounding or fast heartbeat |
| reduced appetite | trouble breathing |
| digestive problems | numbness in the arms or legs |
| difficulty sleeping | seizures |
| restlessness | aggressive behavior |
| dizziness | mania |
| changes in sex drive | paranoia |
| anxiety or panic attacks |
In addition, if you take an excessive amount of Adderall, your body may develop a dependence on the drug. It’s possible to get withdrawal symptoms if you try to cut back or quit using it. Other withdrawal symptoms, in addition to intense cravings for Adderall, may include the following:
fatigue \sagitation \sdepression
problems falling asleep or staying asleep, such as insomnia or excessive daytime sleepiness; you may also experience vivid dreams.
increased desire to eat
movement that is slowed down
a reduced rate of heartbeats
These symptoms may continue for as long as two or three weeks.
Adderall Abuse and Misuse
Misuse of any amphetamine, including Adderall, is always a possibility because of the drug’s widespread availability. People who do not have a prescription for the drug may try to take Adderall in order to boost their ability to focus or in order to stay awake for extended periods of time.
A review of studies
According to research conducted by a Reliable Source, roughly 17 percent of college students have admitted to abusing stimulants such as Adderall.
The effects of the medicine Adderall can be beneficial if it is used in accordance with the directions. However, the effects can be harmful to persons who do not have ADHD but who use the medicine without the supervision of a medical professional.
Even if you have a valid prescription for Adderall, it is still possible to abuse the medication by either taking an excessive amount of it or using it in a manner that was not intended for its usage.
Conclusion
Depending on the type of detection test that is performed, traces of Adderall might be found in your system for up to three days or up to seventy-two hours after your last use of the drug.
The amount of time that the medication remains in your system is dependent on a wide variety of factors, such as the dosage, the rate of metabolism, your age, the function of your organs, and additional factors.
If you have any questions or concerns about Adderall, it is imperative that you speak with either your physician or your pharmacist.


