Table of Contents
Congestive Heart Failure: Symptoms, Causes, and More
What are the 4 stages of congestive heart failure?What is the main cause of congestive heart failure?How long can you live with congestive cardiac failure?Is congestive heart failure very serious?congestive heart failure symptoms,congestive heart failure treatment,congestive heart failure causes,congestive heart failure pathophysiology,congestive heart failure diagnosis,congestive heart failure life expectancy,congestive heart failure stages of dying,congestive heart failure vs heart failure,congestive heart failure symptoms,congestive heart failure treatment,congestive heart failure causes,congestive heart failure pathophysiology,congestive heart failure diagnosis,types of heart failure,congestive heart failure symptoms,congestive heart failure in dogs,congestive heart failure stages of dying,congestive heart failure treatment,congestive heart failure leg cramps,congestive heart failure cough,congestive heart failure life expectancy,congestive heart failure in dogs stages,congestive heart failure icd 10,pictures of swollen ankles due to congestive heart failure,what are the 4 stages of congestive heart failure,signs of congestive heart failure,dog congestive heart failure when to put down,how long can you live with congestive heart failure,stage 5 congestive heart failure,life expectancy of 85-year old with congestive heart failure,leaking legs congestive heart failure,how to comfort a dog with congestive heart failure,can congestive heart failure be reversed
Congestive heart failure, also known as CHF, is a chronic ailment that worsens with time and affects the ability of your heart muscle to pump blood throughout your body.
CHF is a more specific term for the stage of heart failure that is commonly referred to as just heart failure. This stage occurs when fluid accumulates within the heart and causes it to pump less effectively.
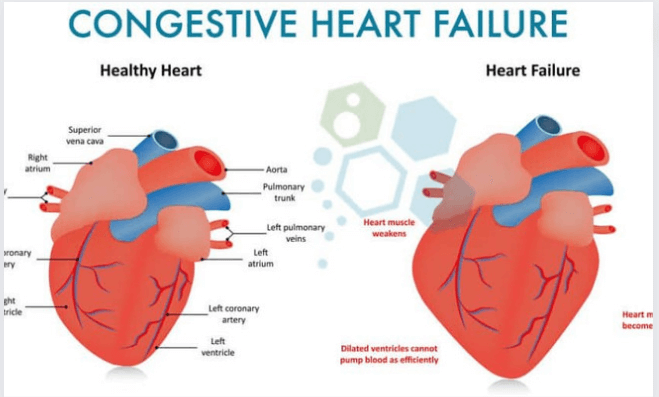
There are four chambers in the heart. The two atriums and the two ventricles make up the upper and lower halves of your heart, respectively. Your ventricles are located in the lower portion of your heart.
The atria are responsible for receiving blood from the body as it is pumped back to the heart from the rest of the body by the ventricles. The ventricles are responsible for pumping blood to the organs and tissues of the body.
When your ventricles are unable to pump enough blood volume to the body, congestive heart failure will occur. At some point in time, blood and other fluids might begin to accumulate inside your:
lungs
abdomen
liver
lower body
CHF is a condition that can be fatal. Seek emergency medical attention if you have any reason to suspect that you or someone you know may have CHF.
What signs and symptoms point to the presence of congestive heart failure?
If you have CHF and are in the early stages of the disease, it is unlikely that you will see any changes in your health. In the event that your disease continues to worsen, you will notice subtle changes in your body.
DO NOT MISS: Skin Tag Removal: Home Remedies, OTC Options, and more
| Symptoms you may notice first | Symptoms that indicate your condition has worsened | Symptoms that indicate a severe heart condition |
| fatigue | irregular heartbeat | chest pain that radiates through the upper body |
| swelling in your ankles, feet, and legs | a cough that develops from congested lungs | rapid breathing |
| weight gain | wheezing | skin that appears blue, which is due to lack of oxygen in your lungs |
| increased need to urinate, especially at night | shortness of breath, which may indicate pulmonary edema | fainting |
Pain in the chest that spreads to other parts of the upper body may also be a warning of an impending heart attack. Seek quick medical assistance if you encounter this sensation, as well as any other symptoms that could lead to a serious illness affecting the heart.
Children and infants who are exhibiting symptoms of heart failure
Detecting heart failure in newborns and young children can be challenging for medical professionals. Among the possible symptoms are:
poor feeding
high levels of perspiration
a struggle to take a breath
These symptoms are frequently misdiagnosed as colic or a respiratory infection due to their similarity. In children, other symptoms of heart failure include a failure to grow normally and low blood pressure.
You might be able to get a sense of a baby’s racing heartbeat through the baby’s chest wall when the baby is at rest.
What kind of treatment is there for congestive heart failure?
Your overall health and the severity to which your problem has advanced will both play a role in determining which treatments you and your doctor will consider.
Medications for congestive heart failure
There are several different drugs, like ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and others, that can be utilized in the treatment of CHF.
Inhibitors of ACE.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors widen blood arteries that have become constricted, which results in an increase in blood flow. Vasodilators are an additional choice to consider in the event that you are unable to tolerate ACE inhibitors.
You might be given a prescription for either of the following:
benazepril (Lotensin)
captopril (Capoten)
enalapril (Vasotec)
fosinopril (Monopril) lisinopril (Zestril) quinapril (Accupril).
ramipril (Altace)
moexipril (Univasc)
perindopril (Aceon)
trandolapril (Mavik)
Pfizer initiated a voluntary recall on April 22, 2022, of 5 lots of the medicine Accupril due to the presence of nitrosamine, and the recall was announced by the company. Nitrosamine is a recognized carcinogen that has the potential to cause cancer. It was discovered that the medicine included amounts of nitrosamine that were higher than the Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) as assessed by the FDA. This recall is limited to a select few lot numbers, and it does not apply to all of Pfizer’s Accupril tablet products in any way, shape, or form. If you use Accupril pills, you should discuss the recall with your doctor or pharmacist so that they can assist you in determining whether or not your medicine was affected by the recall.
Because of the possibility of negative interaction, ACE inhibitors should not be taken in conjunction with the following drugs without first seeing a physician:
Diuretics that are gentle on your potassium levels and potassium supplements. These diuretics are known to create an accumulation of potassium in the blood, which can result in irregular heart rhythms. Riamterene (brand name: Dyrenium), eplerenone (brand name: Inspra), and spironolactone are a few examples (Aldactone).
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs). Some nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen, have been shown to cause salt and water retention. Because of this, the effect that the ACE inhibitor has on your blood pressure may be reduced.
This is a condensed version of the list; therefore, you should always see your physician before starting any new drug.
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers are medications that lessen the amount of work that the heart needs to accomplish. They also have the ability to lower blood pressure and slow down an irregular heart rhythm.
It’s possible to accomplish this by
atenolol (Tenormin) bisoprolol (Zebeta)
carvedilol (Coreg) esmolol (Brevibloc) metoprolol (Lopressor)
nadolol (Corgard) \snebivolol (Bystolic) (Bystolic)
Beta-blockers when combined with any of the following drugs, should be taken with extreme caution because of the potential for an adverse reaction:
Medications that have the effect of slowing down the heart rate. The effects on the cardiovascular system, such as a slower heart rate, may become more pronounced. Verapamil, diltiazem, digoxin, and amiodarone (brand name Nexterone) are some examples of antiarrhythmic medications.
Albuterol inhalation (AccuNeb). Beta-blockers have the potential to completely nullify the effects that albuterol has on bronchodilation.
Antipsychotics. Some antipsychotic medications, such as thioridazine (Mellaril), have been linked to an increased risk of low blood pressure in some patients.
Fentora (Fentanyl). This could result in a drop in blood pressure.
Clonidine (Catapres). The use of clonidine may increase the likelihood of experiencing a sluggish heart rate.
It’s possible that certain drugs are missing from this list. Before beginning treatment with any new medicine, you should always discuss your options with your primary care physician.
YOU MAY LIKE THIS: How Long Does Adderall Stay in Your System? Everything You Need to Know
Diuretics
The amount of fluid in your body can be reduced by taking diuretics. Your body may hold onto more fluid than it should if you have CHF because of the disease.
Your physician might suggest that you:
Loop diuretics. These trigger an increase in the kidneys’ output of urine. This assists in flushing out the excess fluid that has built up in your body. Furosemide (brand name: Lasix), ethacrynic acid (brand name: Edecrin), and torsemide are a few examples (Demadex).
Potassium-sparing diuretics. These aid in the elimination of fluids and sodium while enabling the body to hold onto potassium. Triamterene (brand name: Dyrenium), eplerenone (brand name: Inspra), and spironolactone are a few examples (Aldactone).
Thiazide diuretics. These encourage blood vessels to dilate, which assists the body in getting rid of any excess fluid that may have built up. Examples include metolazone (Zaroxolyn), indapamide (Lozol), and hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide).
Diuretics should be taken with extreme caution when combined with any of the following drugs, as an unpleasant reaction to either one of them is possible:
inhibitors of the ACE. Lisinopril (Zestril), benazepril (Lotensin), and captopril are all examples of medications that have the potential to lower blood pressure (Capoten).
Tricyclics. They are also known as tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and they have the potential to produce a drop in blood pressure. Amitriptyline and desipramine are two examples of such medications (Norpramin).
Anxiolytics. Anxiolytics are a kind of anti-anxiety medication that has been shown to have a hypotensive effect. Common anxiolytics include alprazolam (Xanax), chlordiazepoxide (Librium), and diazepam (Valium) (Valium).
Hypnotics. There is a possibility that sedatives like zolpidem (Ambien) and triazolam (Halcion) will lower one’s blood pressure.
Beta-blockers. Beta-blockers like metoprolol (which is sold under the brand name Lopressor) and carvedilol (which is sold under the brand name Coreg) may also produce low blood pressure.
Calcium channel blockers are medications. A decrease in blood pressure is a potential side effect of using CCBs. Examples include amlodipine (Norvasc) and diltiazem (Cardizem).
Nitrates. Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat) and isosorbide-dinitrate (Isordil) are two examples of medications that have the potential to reduce blood pressure.
NSAIDs. There is a possibility that these drugs will be harmful to the liver.
This is a condensed list that only includes the most typical drug-to-drug interactions. Before beginning to take any new medications, you should consult with your primary care physician first.
Surgical operations and other procedures
If the prescribed treatments are not producing the desired results, more intrusive procedures can be necessary.
One treatment option is called angioplasty, which is a technique that opens up blocked arteries.
In order to assist your heart valves in opening and closing in the appropriate manner, your cardiologist might possibly recommend heart valve repair surgery.
Symptoms of congestive heart failure in their early stages
As was previously discussed, the early warning signals of congestive heart failure may not present themselves in a particularly obvious manner. The following are some early warning indicators that you should discuss with your source of healthcare:
fluid retention in bodily tissues such as the ankles, feet, legs, or abdomen, coughing or wheezing, shortness of breath, and weight increase for no apparent reason that cannot be linked to anything else
general tiredness
an accelerated rate of heartbeat
symptoms such as loss of appetite or feeling queasy
experiencing feelings of confusion or disorientation
HERE MORE: How Long Does Nicotine Stay in Your System? Everything You Need to Know
Congestive heart failure stages
| Stage | Main symptoms | Outlook |
| Class 1 | You don’t experience any symptoms during typical physical activity. | CHF at this stage can be managed through lifestyle changes, heart medications, and monitoring. |
| Class 2 | You’re likely comfortable at rest, but normal physical activity may cause fatigue, palpitations, and shortness of breath. | CHF at this stage can be managed through lifestyle changes, heart medications, and careful monitoring. |
| Class 3 | You’re likely comfortable at rest, but there’s a noticeable limitation of physical activity. Even mild exercise may cause fatigue, palpitations, or shortness of breath. | Treatment can be complicated. Talk with your doctor about what heart failure at this stage may mean for you. |
| Class 4 | You’re likely unable to carry on any amount of physical activity without symptoms, which are present even at rest. | There’s no cure for CHF at this stage, but there are still quality of life and palliative care options. You’ll want to discuss the potential benefits and risks of each with your doctor. |
What are the causes of CHF?
CHF can be caused by different health issues that have a direct impact on the cardiovascular system of the patient. Checkups once a year are recommended for this reason, since they help reduce the risk of a number of issues related to heart health, including the following:
hypertension; high blood pressure (hypertension)
disease of the coronary arteries
valve conditions
Hypertension
CHF is a risk factor for developing when your blood pressure is significantly higher than what is considered normal.
There are a variety of factors that might lead to hypertension. One of these is the hardening of your arteries, which results in an increase in the blood pressure inside your arteries.
Disease of the coronary arteries
The coronary arteries, which are the tiny arteries that provide blood to the heart, can get obstructed by cholesterol and other types of fatty substances. Because of this, the arteries become more constricted.
Blood flow is restricted by coronary arteries that are narrower, which can lead to damage in the arteries themselves.
Valve conditions
The valves in your heart are responsible for controlling the flow of blood through your heart by opening and closing to allow blood to enter and exit the chambers.
If your valves do not open and close in the proper manner, this could cause your ventricles to have to work harder to pump blood. It’s possible that an infection or defect in the heart is to blame for this.
Other requirements also apply
There are a number of problems that may raise your chance of developing CHF, including some that are seemingly unrelated to the heart but can lead to CHF nonetheless.
These are the following:
Certain chemotherapeutic medications are used to treat diabetes, thyroid illness, and obesity.
There is some evidence that severe infections and allergy responses could possibly lead to congestive heart failure.
Which kinds of CHF are the most frequently encountered?
The most prevalent form of CHF is known as left-sided CHF. It takes place when your left ventricle is unable to pump blood effectively to the rest of your body.
As the disease continues, fluid can begin to build up in your lungs, which can make it harder for you to breathe.
There are two different types of heart failure that affect the left side:
When the left ventricle is unable to contract regularly, a condition known as systolic heart failure can develop. Because of this, there is less force available to propel blood through the circulatory system. Without this force, the heart will not be able to pump blood effectively.
Diastolic dysfunction, also known as a diastolic failure, is the condition that occurs when the muscle in the left ventricle becomes rigid. In the spaces in between beats, the heart is unable to completely fill with blood because it can no longer rest.
When the right ventricle of the heart struggles to pump blood to the lungs, a condition known as right-sided congestive heart failure (CHF) can develop. Your blood arteries become blocked, which results in fluid retention in your lower extremities, belly, and other essential organs. This condition is known as venous insufficiency.
Both left-sided and right-sided CHF are not mutually exclusive states; they can coexist. In most cases, the sickness manifests itself on the left side first, and if it is not treated, it will eventually spread to the right.
Life expectancy
Between the years 2013 and 2016, there were approximately 6.2 million adults in the United States who suffered from heart failure.
Report
According to a reliable source from the American Heart Association, around fifty percent of patients who have been diagnosed with CHF will still be alive after five years.
A previous study
According to the findings that were presented by Reliable Source, people with a lower risk who were diagnosed before the age of 50 had life spans of approximately 20 years after the diagnosis.
There were a number of factors that led to variations in life expectancy, including age at the time of diagnosis, underlying diseases, and sex. Some people lived less than three years after their diagnosis.
The prognosis and life expectancy of a patient with congestive heart failure might vary widely due to the many different factors that contribute to the condition. In most cases, getting an early diagnosis and adhering to a treatment plan can result in improved disease control and a longer lifespan.
ALSO READ: How Long Does Alcohol Stay in Your System? Everything You Need to Know
What tests are done to detect CHF?
After you have discussed your symptoms with your primary care physician, he or she may decide to refer you to a cardiologist for further evaluation.
During the physical exam, the cardiologist will listen to your heart using a stethoscope in order to diagnose any irregular heart rhythms that may be present.
Your cardiologist will likely request a series of diagnostic procedures to validate an initial diagnosis. These tests will look at the chambers, blood arteries, and valves of your heart.
The diagnosis of heart issues can be determined by a number of different types of tests. Due to the fact that these examinations measure a variety of things, your physician may suggest getting more than one done in order to get a comprehensive view of your health.
Blood tests
Examining the patient’s blood can detect abnormal blood cells as well as infections. This includes checking the patient’s blood count as well as their kidney function and liver function. In addition to this, they can assess the amount of BNP, which is a hormone that is elevated in patients who have heart failure.
X-ray of the chest
X-rays of the chest can be used to evaluate the size of the heart as well as the amount of fluid buildup in the lungs and blood vessels. This is typically one of the very first tests that your physician would suggest to you.
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram, often known as an EKG or ECG, is a recording of your heart’s electrical activity.
There is a possibility that the walls of the chambers in your heart are thicker than they should be if you have abnormalities in your heart’s rhythm, such as a rapid heartbeat or an irregular rhythm. That can be a clue that you’re about to have a heart attack.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a recording of the structure and motion of the heart that is created by using sound waves. If you already have poor blood flow, damaged muscles, or a heart muscle that doesn’t contract regularly, the test can determine all of these things for you.
Exam under pressure
The results of stress testing provide information on how well your heart operates under varying degrees of pressure.
The increased workload on your heart makes it simpler for your physician to identify any potential issues.
catheterization of the heart
Cardiac catheterization has the ability to reveal any blockages in the coronary arteries. Your physician will start the procedure by inserting a thin tube into one of your blood vessels from your upper thigh (the area around your groyne), arm, or wrist.
At the same time, the medical professional can examine the blood flow and pressure in your heart chambers, as well as take blood samples, observe your coronary arteries via x-ray, and view your coronary arteries.
MRI
Images of your heart can be taken with an MRI. Your doctor will be able to determine whether or not there is damage to your heart by looking at both still and moving photographs.
How to avoid getting congestive heart failure in the first place
Although our genetics can influence some aspects of our health, our lifestyle choices can also have an impact.
You can reduce your risk of developing heart failure, or at the very least, you can delay its onset, by doing a few different things.
Avoid or quit smoking
If you currently smoke and haven’t been successful in quitting, talk to your doctor about getting recommendations for helpful products and services.
The inhalation of secondhand smoke also presents a health risk. If you share your home with someone who smokes, you should ask them to do so outside.
Ensure that your diet is healthy and well-balanced.
A diet that is good for your heart should be high in vegetables, fruits, and grains that are whole. You also need protein in your diet.
Avoid doing these things at all costs:
salt (sodium) added sugars
solid fats
granulated cereals
Physical activity Improving your heart health can take as little as one hour of moderate aerobic activity seven days a week. Getting some exercise through activities like walking, cycling, and swimming are all beneficial.
If you haven’t been active for a while, you should begin by exercising for only 15 minutes every day and gradually increase the amount of time you spend exercising.
If you find that you lack the motivation to exercise on your own, you might want to think about enrolling in a class — which can even be done online — or getting personal training at a gym in your area.
Keep an eye on your weight.
Being obese or overweight can put a strain on your heart and cause other health problems. Maintain a nutritious diet and a consistent exercise routine.
Consult a medical professional about the best way to go if your current weight is not compatible with the needs of your body. You also have the option of speaking with a dietician or nutritionist.
Other precautionary measures
Consume alcoholic beverages in moderation and steer clear of drugs that are unlawful. When taking prescription medications, make sure to carefully follow the included directions, and under no circumstances should you ever raise your dose without first consulting with your physician.
You are able to carry out these steps even if you have a high probability of developing heart failure or if you already have some heart damage. Make sure you ask your doctor how much exercise is okay for you to perform and if there are any additional limitations you need to follow.
If you suffer from high blood pressure, heart disease, or diabetes, it is imperative that you take your prescription precisely as prescribed. Visit your doctor on a consistent basis to keep track of your condition and report any new symptoms as soon as possible.
What should I anticipate happening in the long run?
Your condition might get better if you take certain medications, have surgery, or make some adjustments to your lifestyle. Your prognosis is contingent upon the stage of your congestive heart failure as well as the presence of any other co-existing illnesses, such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
The earlier that a problem is detected, the better the prognosis for the patient. Talk to your healthcare provider about the therapy option that will benefit you the most.


